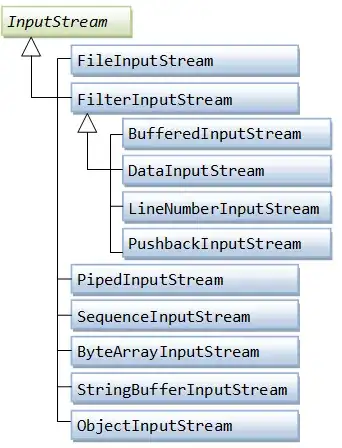
In the below server socket program, byte stream object is used to read data from client, as mentioned - InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
public class SingleThreadTCPServer{
ServerSocket serverSocket;
int serverPort = 3333;
public SingleThreadTCPServer(){
try{
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(serverPort);
System.out.println("ServerSocket: " + serverSocket);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void listen(){
try{
while(true){ //run until you terminate the program
//Wait for connection. Block until a connection is made.
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Socket: " + socket);
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
int byteRead;
//Block until the client closes the connection (i.e., read() returns -1)
while((byteRead = in.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)byteRead);
}
}
}catch(IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new SingleThreadTCPServer().listen();
}
}
I had been through the implementation of getInputStream() method but could not understand the actual subtype of InputStream object that is actually returned from getInputStream()
Among the below subtypes,
Which is the actual stream type that is being used by server to read data from client?