As web developers, we all learn that sessions help overcome the problems related to the stateless nature of HTTP. We create a unique session id, and send it to the browser -- and when the browser sends the same id back to us, we identify the user easily.
All this sounds pretty straightforward, and NOT so complicated to implement in any language.
NOW
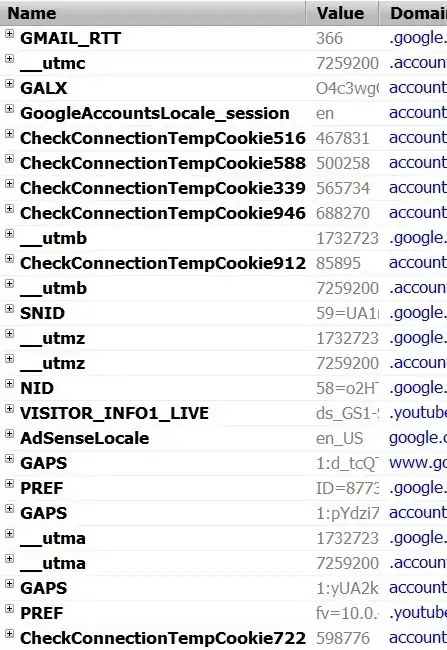
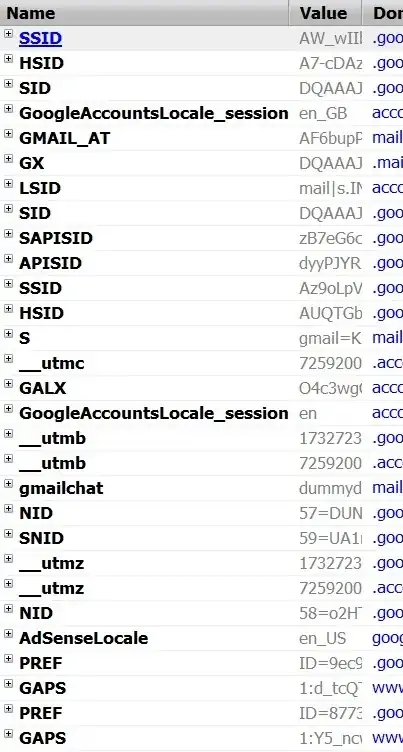
Look at the following screenshots I took. These show the kinds of cookies popular websites store. It looks like they are storing multiple session IDs, or they are trying the hide the actual id by setting so many cookies, or, it is something very specialized security measures they're taking to prevent session hijacking and other related problems. Or, whatever.
Gmail (before login)
Gmail (after login)
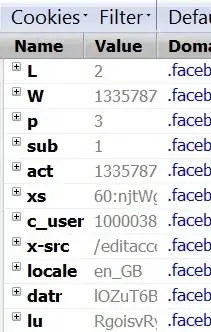
StackExchange
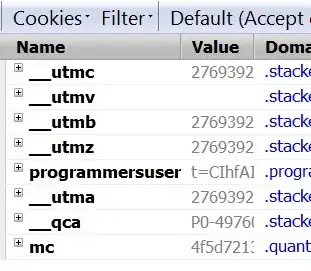
(Don't worry, you can't steal my session -- it's stale and incomplete :))
So, my question is -- what purpose does this complicatedness serve? Please explain what these different cookies mean (in general), and for what purposes these are set. Lastly, hint on how I can do it (and whether I should) in my own apps.
One more question: In a lot of instances, the values in the cookies look like they are URL-encoded -- why so?