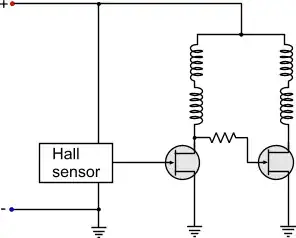
Your question seems to center around the use of the Hall Effect sensor in a 2-wire fan. I believe what you are asking is, "If the Hall Effect sensor isn't feeding a tachometer signal back to the motherboard, what is it doing?"
In a two wire system, the only signals fed in a voltage and ground. There is no control. So what is it that is alternating the phases and causing the rotation? If it were just a DC signal, the permanent magnet on the rotor would spin until it's magnetic field aligned with that of the coils in the stator and stay in that position.
Instead what happens is, a DC is fed in and it finds the path of least resistance to ground. Assuming the transistor on the left is open, it would flow through the coils and transistor on the right. The rotor spins and the magnetic field passes the Hall Effect sensor. The Hall Effect sensor sees this rotation and turns on the transistor on the left. This side now has a lower resistance so the current flows through it, reversing the field in the stator which pushes the rotor around again. The Hall Effect sensor senses a change in the magnetic field from the continued rotation of the rotor and then turns off the left transistor. Current then flows through the right.
This alternation continues as long as power is supplied and is the source of the alternating magnetic field that causes the rotation of the fan.