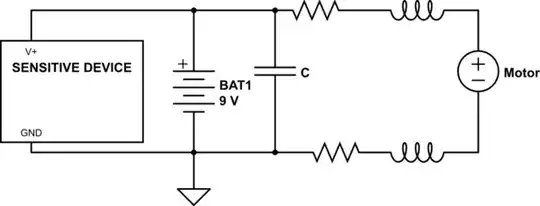
The function of the capacitor is to suppress electromagnetic noise (EMI) that the motor's coils will generate while in operation, due to the contact brushes inside the motor making and breaking the circuit (i.e. commutation). If you search this site, there are several questions covering motor EMI, so I won't detail it here.
Such EMI noise suppression is best done as close to the source of noise as possible. That is why you see the capacitor across the motor leads, and not further away. Even if the entire circuit consists of just the battery and the motor, EMI will radiate from this circuit, and other nearby electronics will be affected.
For instance, if the motor is operated very close to computer speakers with built-in amplifiers, you might be able to hear the noise caused by this motor EMI being radiated.
Regarding resistors: While resistors are often used for current control with LEDs, motors are best not controlled using resistors: The resistor would generate a fair bit of heat, wasting the energy that could be used by the motor.
Resistors are used for current sensing though, in some motor circuits.
 I took apart a sharper image personal fan run by a 9volt battery.
I took apart a sharper image personal fan run by a 9volt battery.