Transconductance is a property of certain electronic components. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance; transconductance is the ratio of the current change at the output port to the voltage change at the input port. It is written as \$g_m\$. For direct current, transconductance is defined as follows:
\$g_m = {\Delta I_\mathrm{out} \over \Delta V_\mathrm{in}} \$
For small signal alternating current, the definition is simpler:
\$g_m = {i_\mathrm{out} \over v_\mathrm{in}} \$
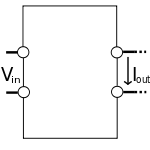
Courtsey of Wikipedia.
It's use is simple: it's used to mathematically model any device where some current is a function of some voltage. Vacuum tubes, field effect transistors, and bipolar transistors can all be modelled as such, as well as many circuits composed of them.
