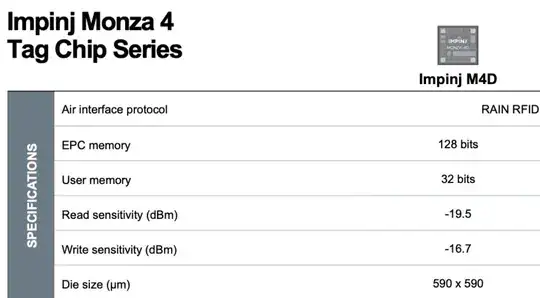
The datasheets of the passive UHF RFID tags mentions the read and write sensitivity values in dBm. I see that the reader transmit power is usually mentioned in watts and dBm values can be converted to watt. However, what does the -sign in this context mean? e.g. see the datasheet below:
-
1You need to study the meaning of the decibel (it can have positive and negative values). – Andy aka Dec 27 '22 at 11:59
1 Answers
The negative sign in dBm indicates that the power level is less than 1 milliwatt (mW). The dBm scale is a logarithmic scale that is used to express the ratio of a power level in milliwatts to a reference power level of 1 milliwatt. The formula for converting a power level in dBm to watts is as follows:
$$\text{Power}(\text{W}) = 1\space\text{mW}\cdot10^\frac{\text{power level in dBm}}{10}\tag1$$
For example, if the power level is -10 dBm, the power in watts is calculated as follows:
$$\text{Power}(\text{W}) = 1\space\text{mW}\cdot10^{-\frac{10\space\text{dBm}}{10}}= 0.1 \space\text{mW} = 100\space\mu\text{W}\tag2$$
The negative sign in dBm is used to indicate power levels that are less than 1 milliwatt. A power level of 0 dBm is equal to 1 milliwatt, and a power level of -10 dBm is equal to 0.1 milliwatts. As the power level decreases, the negative sign becomes more negative, indicating a smaller power level.
The read and write sensitivity values of a passive UHF RFID tag are expressed in dBm because they represent the minimum power level required for the tag to be read or written to by an RFID reader. The read and write sensitivity values are typically expressed as a range, such as -70 dBm to -80 dBm, indicating the minimum and maximum power levels that the tag can operate at.
- 7,203
- 12
- 21