I have a boost converter that takes 3-5V at input and outputs a steady 5V (This one : https://aliexpress.com/item/33046073847.html). I plugged it to my 18650 battery cell so that I can power an Arduino and also charge some peripherals (earbuds, phone, etc). This boost converter can output up to 3A. I was wondering if I would be able to output 6A if I put two of the modules in parallel? My 18650 cell can output up to 30A according to the datasheet.
I'm quite sure the following would work fine :
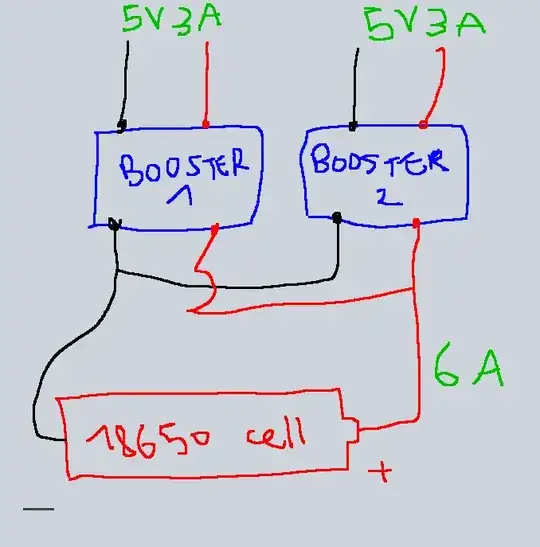
But would the following work as well? :
So my questions basically : can I parallel boosters and expect to earn more current capability? If I put thick wires and put 5 boosters in parallel, will this circuit be able to output steady 5V at up to 15A ?
As far as I know about electronics as a hobbyist, such module is chopping the current (SMPS) and feeding itself a feedback to adapt and output steady 5V. I am wondering if this parallel circuit will (or not) "potentiate" the feedback exponentially and behave erratically.