I've used these in various similar situations, and perhaps one of the would suit your application:
- Edge-triggered interrupt pin on the MCU
- ATTiny25/45/85 as a reset controller feeding an interrupt or reset pin on the MCU (use Tiny's internal oscillator to keep part count down; use its power-on reset and brown-out detector to send whatever signal desired.)
Although an ATTiny seems like overkill, it's sometimes convenient: they are pretty small (6-pin, 8-pin) and $0.25/unit!
It's worth noting that many MCUs (including ATTiny) have brown-out detectors, which are specifically for this kind of application.
At least ATmega328 and ATTiny25 (and I'm sure many others) work like this:
ATmega328P has an on-chip brown-out detection (BOD) circuit for monitoring the VCC level during operation by comparing it to a fixed trigger level. The trigger level for the BOD can be selected by the BODLEVEL fuses. The trigger level has a hysteresis to ensure spike free brown-out detection. The hysteresis on the detection level should be interpreted as VBOT+ = VBOT + VHYST/2 and VBOT– = VBOT – VHYST/2.
...
The BOD circuit will only detect a drop in VCC if the voltage stays below the trigger level for longer than tBOD
- VHYST is 50 mV (Tiny) 80 mV (Mega)
- VBOT is 2.7 ± 0.2 V or 4.3 ± 0.3 V, chosen in configuration fuses (also 1.8 V on ATTiny).
- tBOD is a few microseconds, 2μs on ATTiny.
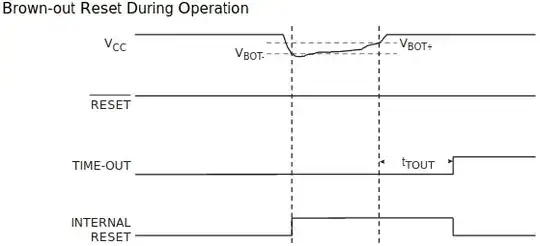
(image and quote from Atmel datasheets)
Many other MPUs' brown-out detectors will have very similar properties, though of course the details will vary.