If you use the correct terminology much confusion can be dispelled.
The devices you are referring to are not "chargers". They are laptop power supplies.
The "charger" is part of the laptop and is integrated with the battery management system. This means that, in general, it should be safe to power a laptop from a power supply with the correct DC voltage output and adequate current rating (greater than or equal to the laptop's requirement).
The problem arises in that many manufacturers protect the power supplies by adding a third pole to the connector to signal the power supply's rating to the laptop. There are various schemes such as a fixed voltage or a serial transmission over the extra wire to the laptop.
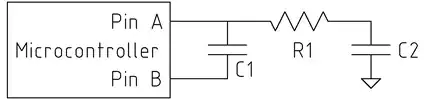
Figure 1. A random web image showing power connector pinout for Lenovo laptops using the yellow rectangular plug. The resistor, which is in the power supply, will be used by the laptop charging circuitry to determine the power capability of the PSU. If it meets or exceeds the power requirement of the laptop then charging will be enabled. Otherwise the laptop will run on "mains" only. Image source: Lenovo power supply plug configuration on YouTube.
In some cases - I'm familiar with the older Dell laptops - the laptop could be powered by any of their power supplies with the right connector but would only charge when they identified that the power supply was capable.
When and why is it safe to use a specific laptop charger for another laptop?
- When the voltage is right.
- When the PSU can supply adequate current.
- Optionally, when the handshaking is correct.
This varies from device to device so you will have to expand your knowledge for the brand and models in question. You will also need to be content in the knowledge that you are voiding any warranty still left on the laptop or power-supply.
