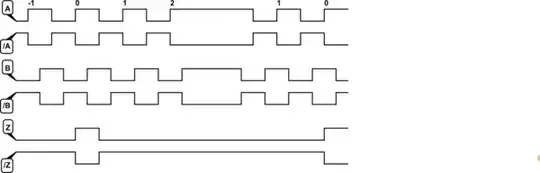
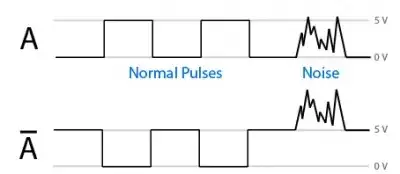
I have a sensor that has 3 components: X, Y and Z and for every component there are 2 channels:
- X+ :0 V ± 5 V voltage output
- X- :0 V ± 5 V voltage output inverted
All I know is :
- If the circuit uses "active high" logic, 5 volts represents a digital "1" and 0 volts represents a digital "0".
- If the circuit uses "active low" logic, 5 volts represents a digital "0" and 0 volts represents a digital "1".
My question is: what's the purpose of the inverted output? How can I make use of it as I am plotting results.