I'm going to be looking at a few products that have failed EMC radiated emissions testing and will need to apply fixes in order to make them pass (unfortunately, in these cases, two of the designs can't be modified to fix the problem at board level).
NOTE To see high resolution images of the scans, right click on the images and open in a new tab/window
In my particular case, the problems seem to stem from the following:
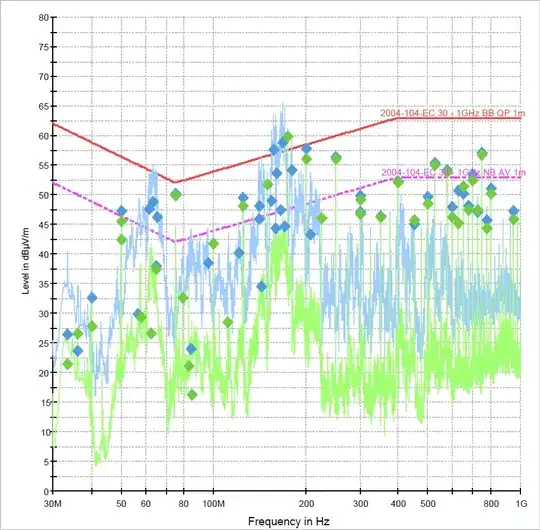
- Product 1 is in a metal enclosure with a cut out for a TFT display and keypad, and several cables running out of the enclosure. The system is microcontroller based, with unshielded power, shielded CAN and shielded RS232 interfaces exiting the enclsoure. The problem seems to be coming from a 25MHz crystal that is driving the graphics controller and is leaking out from the cables and also from the front of the screen.
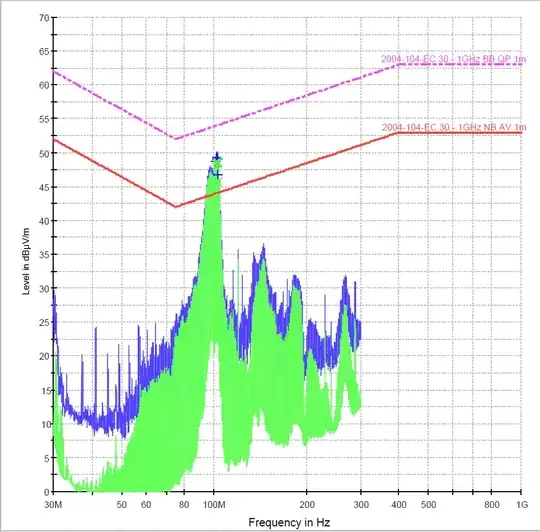
- Product 2 is also in a metal enclosure but with a plastic window and cables running out. This system is microprocessor based (Linux) with unshielded power, shielded CAN and shielded RS232 interfaces exiting the enclosure. The problem in this cases appears to be stemming from the 3A, 5V switching power supply on the board (Lot's of 3kHz harmonics). There's also a lot of 45MHz harmonics stemming from the SD card. This product is open to design modifications
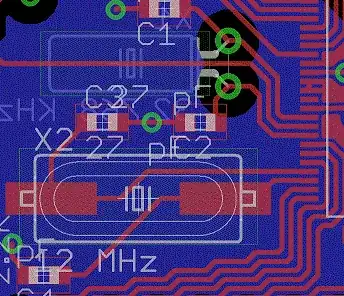
- Product 3 is in a plastic enclosure with a large plastic window for indicators and cables running out. The system is microcontroller based with unshielded power, shielded CAN and unshielded GPIO interfaces exiting the enclosure. The problem seems to be stemming also from the same 3A , 5V switching power supply (same design as the previous item).
All three products are double layer boards.
What steps can I take and what solutions can I use to help reduce the radiated emissions of this existing design? What reference material (books, articles etc) can I use that discuss this topic?