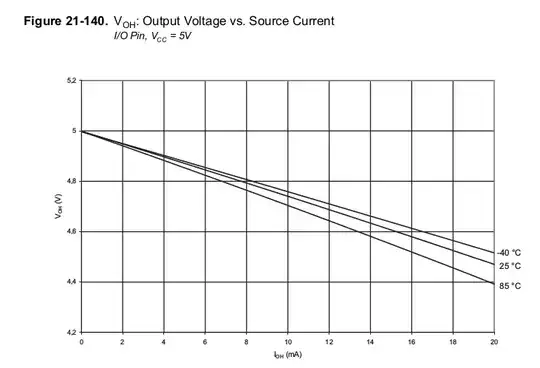
For example, when driving a logic-level MOSFET directly from a microcontroller, what is the smallest gate resistor that can be used?
Specifically for AVR microcontrollers; i.e. this datasheet, the maximum current that can be sourced or sunk from a pin is 40mA, for a logic-level MOSFET where the gate is driven between ground and +5V, this would mean a gate resistor of at least 125 Ohms is necessary.
However, I also see other anecdotal evidence (not in the datasheet) that the pin itself has an internal resistance of 25 Ohms; this would mean that only 100 Ohms is necessary for the gate resistor.
I can't find any references to this internal resistance in the datasheet; but it does seem to have some value. Are there any canonical references?