Starting here:
http://hypertextbook.com/facts/1998/TreshaEdwards.shtml
"Over land the average electric field is about 120 V/m …. Assuming an exponential increase of the conductivity with altitude, it can be shown that the electric field decreases exponentially with altitude. At the 30-km level, the electric field is as low as 300 MV/m [sic]. Integrating the electric field from the earth's surface to the ionosphere gives as a result an electric potential difference of about 200 kV." Standardized result: 0.300–120 V/m
Since this is the case, how come a conductor placed in this field doesn't immediately have a powerful current running through it?
This is my primitive understanding of the situation:
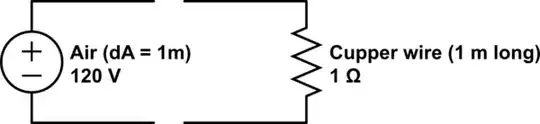
simulate this circuit – Schematic created using CircuitLab
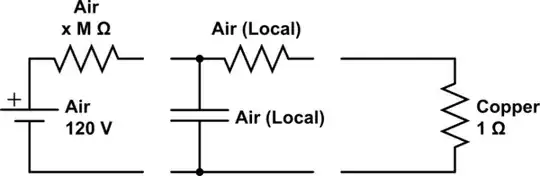
But clearly this must be wrong, because you don't get 120 Amps through any random string of wire that happens to hang vertically so what am I missing?
EDIT
Is this a more reasonable approximation?